How to Write Smarter ChatGPT Prompts: Techniques & Examples

As AI tools like ChatGPT and Claude become more common, knowing how to write good prompts has become a valuable skill. This is where prompt engineering plays an essential role because it deals with figuring out how to ask an AI the right question, which can make the difference between a helpful and confusing answer..
Writing smarter prompts means crafting inputs that are context-rich, ethically sound, goal-specific, and tailored to how LLMs like ChatGPT interpret instructions—not just well-written, but strategically designed.
This article explores how to write smarter ChatGPT prompts by applying critical thinking and using context effectively. Through real-world examples, practical strategies, and actionable tips, you’ll learn how to craft prompts that make AI responses more accurate, relevant, and responsible.
As the demand for skilled prompt engineers rises, especially in workplaces, professionals increasingly turn to structured learning paths like ChatGPT for Working Professionals and Master Generative AI to develop a stronger foundation in critical thinking, AI behavior, and prompt design.
To make high-quality learning more accessible, Great Learning has recently launched Academy Pro, a new subscription plan that unlocks unlimited access to all premium courses for just ₹799 per month. With this update, learners no longer need to purchase premium courses individually, making continuous upskilling more affordable than ever.
Foundations of Smarter Prompting: Prompt Engineering + Critical Thinking
Writing smarter ChatGPT prompts begins with two core skills: understanding how prompts shape AI behavior, and applying critical thinking to craft them with intent, clarity, and context.
Prompt engineering is the practice of crafting inputs that help AI models, like large language models (LLMs), generate useful and relevant responses. Because these models rely solely on text instructions, the wording, structure, and level of detail in a prompt directly affect the response.
Different types of prompting serve different goals:
- Zero-shot prompting gives the model a direct command without examples (e.g., “Write a short poem about the ocean”).
- Few-shot prompting includes examples to demonstrate the desired pattern.
- Chain-of-thought prompting encourages the model to “reason” step-by-step by asking it to break down its thinking.
While each method varies in style, they all rely on clarity and intent. A vague prompt like “Tell me about space” often leads to generic answers. A smarter alternative might be:
“Give me three interesting facts about black holes, written for a 10-year-old.”
That extra context- audience, structure, tone; makes a dramatic difference.
But smart prompting goes beyond structure. It requires critical thinking: the ability to ask the right questions, evaluate assumptions, and anticipate how the AI will interpret your request.
Consider the difference:
- Basic prompt: “Write an article about climate change.”
- Smarter prompt: “Write a 300-word explainer on climate change for high school students, using simple language and real-world examples.”
The second prompt shows deeper reasoning. It accounts for audience, tone, length, and learning goals, all key to guiding the model more effectively.
Smart prompting is an iterative process. You assess what you’re trying to achieve, test different versions, and revise as needed. This mindset reduces trial and error and leads to higher-quality outputs faster.
By combining prompt engineering techniques with critical thinking, you don’t just communicate with AI more clearly, you guide it more intelligently. This is the foundation of writing smarter prompts.
If you’re just starting out or want hands-on exposure to different prompting methods, the free course Prompt Engineering for ChatGPT offers a practical primer on the mechanics and types of prompts used in real-world scenarios.
For those looking to build stronger reasoning and decision-making frameworks in AI tasks, Great Learning’s AI and ML Program with Great Lakes emphasizes critical thinking in AI use cases and project-based problem solving.
The Role of Context in Prompt Engineering


In prompt engineering, context is everything. It is the background info that will assist the AI in knowing what you are asking and why.
This may be the user’s intent, the task domain (i.e., legal, medical, creative writing), previous conversation history, the required tone, or condition specific to the substance, such as the number of words or format, etc.
Even a well-written query can come flat with lack or uncertainty. The AI might give you a generic answer or head in the wrong direction entirely. However, when context is provided, responses tend to be more accurate, relevant, and natural.
For example, take the simple prompt:
“Summarize this article.”
Without context, the AI doesn’t know the audience, the tone, or how much detail is expected. Now compare that with:
“Summarize this article in 3 bullet points for a time-strapped executive who needs key takeaways.”
Suddenly, the AI has more to work with, and the result will likely be sharper and more useful.
Context also matters in more prolonged interactions. If you’re working on a multi-step task or referencing earlier messages, the model performs better when that history is clearly included or echoed in your prompt.
Good prompt engineers don’t just tell the AI what to do they help it understand the bigger picture. That differentiates between a generic reply and one that truly fits the task.
Whether you’re building educational tools or business chatbots, understanding domain-specific context is key. Courses like Generative AI on Microsoft Azure explore how to incorporate enterprise-level context into LLM prompts effectively.
Smarter Prompting Strategies
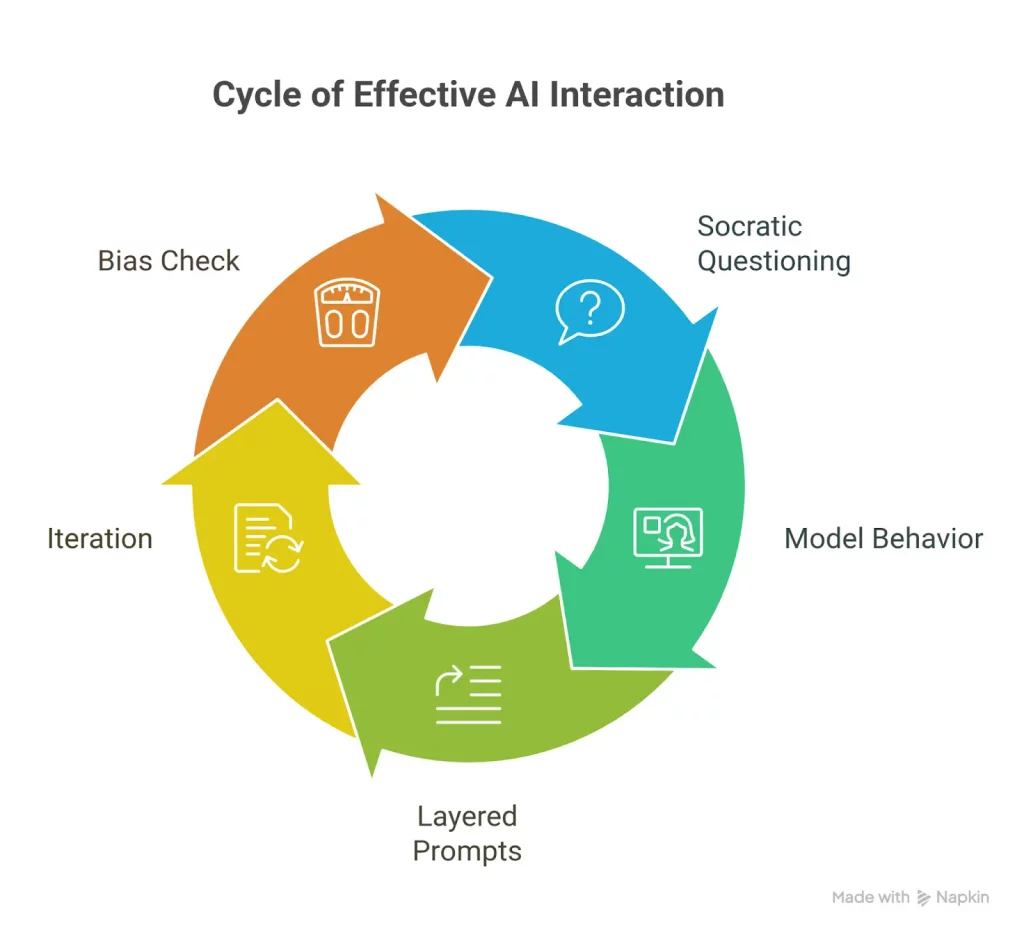

Designing effective, context-aware prompts requires more than just knowing how the model works. It takes deliberate, reflective thinking. Here are some strategies grounded in critical thinking that can help you write better prompts.
1. Ask Socratic Questions
Start with the basics: What am I trying to achieve? Who will use this output? A prompt for a technical report will differ significantly from one meant for a beginner. Asking these questions helps you clarify your intent and tailor the prompt accordingly.
2. Anticipate the Model’s Behavior
AI models don’t “understand” in the human sense. They respond to patterns. So it helps to test how small changes in your prompt affect the output. Try variations, check for unexpected results, and don’t assume the model will read between the lines.
3. Layer the Prompt with Explicit Context
Don’t rely on the AI to guess. If something is important like tone, structure, or target audience, spell it out. For example, instead of saying “Write a summary,” say “Write a concise, professional summary for a business newsletter.”
4. Iterate and Refine
One prompt won’t be perfect on the first try. Use an iterative loop: prompt → evaluate → adjust. Each round helps you get closer to the desired result while revealing what works and what doesn’t.
5. Watch for Bias, Ambiguity, and Assumptions
AI models reflect patterns in their training data. That means they can unintentionally reinforce stereotypes or give vague, overly generic responses. Critical thinkers spot these issues and adjust prompts to steer the model in a better direction.
These strategies are not only for power users but also critical for anyone who wants more control and clarity when using generative AI.
Real-World Examples & Case Studies
Case 1: Customer Support Chatbot — Context-Aware Prompting to Deflect Complaints
A delivery company’s AI chatbot was designed to handle customer complaints.
Initially, the prompt was:
“Respond to customer complaints professionally.”
However, this led to generic and sometimes inappropriate responses.
After refining the prompt to:
“Respond to customer complaints with empathy, acknowledge the issue clearly, and offer a next step. Keep the tone calm and reassuring,”
The chatbot’s performance improved significantly. This adjustment led to more personalized and effective interactions, aligning with findings that context-aware chatbots can enhance customer satisfaction by recalling past interactions and providing relevant suggestions.
These scenarios mirror those explored in the ChatGPT for Customer Support course, which focuses on empathetic, efficient prompt design for real-world complaint management.
Case 2: Educational Tutor — Adjusting for Tone and Prior Knowledge
The initial prompt, “Explain how photosynthesis works,” resulted in overly technical explanations.
By modifying the prompt to:
“Explain how photosynthesis works in simple terms, as if you’re teaching a high school student seeing it for the first time. Use analogies and examples,”
The AI provided more accessible and engaging content. This approach aligns with research emphasizing the importance of personalization and adapting explanations based on the learner’s prior knowledge.
These cases underscore the significance of critical thinking in prompt engineering. By thoughtfully considering context, audience, and desired outcomes, prompts can be crafted to elicit more accurate and relevant AI responses.
Best Practices Checklist
Designing effective, context-aware prompts takes both skill and thoughtful reflection. Here’s a quick checklist of best practices to guide your process:
- Understand the user’s needs
Before crafting a prompt, clarify who it’s for and what they’re trying to achieve.
Don’t assume the AI “gets it.” Spell out background details, desired tone, audience, and format.
Try different versions of your prompt. See how minor tweaks change the output, and refine based on what works.
When the model gives a poor result, ask why. Was the prompt too vague? Too broad? Learn from what didn’t work.
Avoid prompts that may unintentionally reinforce bias or misinformation. Think about the social impact of the output.
By applying these practices regularly, you can create prompts that perform better and align with real-world goals and values.
Conclusion
Writing smarter ChatGPT prompts isn’t just about technical know-how; it’s about thoughtful design. By combining critical thinking with clear context and intentional structure, you can guide AI to deliver more accurate, relevant, and meaningful responses.
Whether you’re generating content, solving problems, or supporting users, smarter prompting starts with asking the right questions:
Who is this for? What exactly do I need? What could be misunderstood?
The more you experiment, analyze, and refine your approach, the more skilled you become at crafting prompts that unlock the full potential of tools like ChatGPT.
Smarter prompts lead to smarter results, and that’s what makes the difference.










![How to Explain Reasons for Job Change in Interviews? [2024]](https://metaailabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Explain-Reasons-for-Job-Change-in-Interviews-2024.png)