ChatGPT hits nearly 4 billion monthly visitors as growth slows to a crawl
OpenAI’s chatbot reached 3,905 billion visitors last month, marking a new record even as monthly growth nearly stalled.
ChatGPT saw 3,905 billion visitors in February 2025, according to data from Similarweb. While this represents a new high, it’s only 1.44% more than January’s numbers. Year-over-year growth remains strong at 137% compared to February 2024.
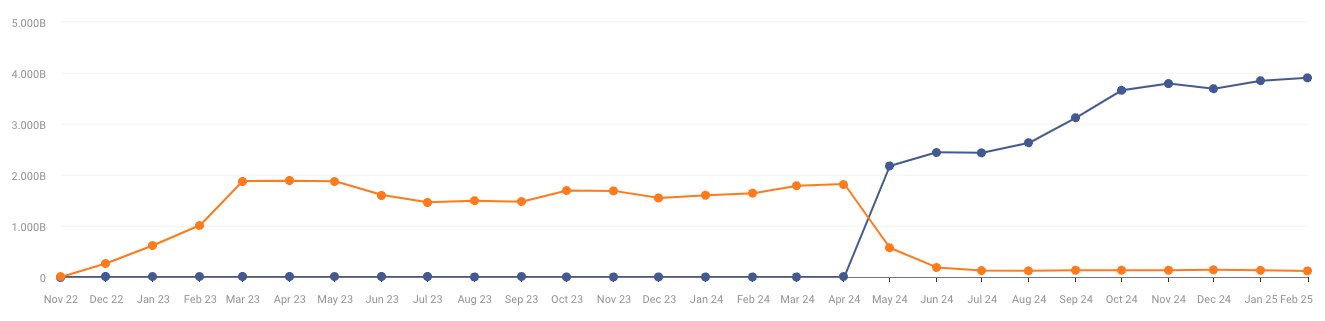
These numbers have pushed ChatGPT up the global rankings. The AI chatbot now ranks fifth among desktop websites worldwide and seventh when combining desktop and mobile traffic.
ChatGPT reportedly ended 2024 with 15.5 million paying subscribers, up significantly from 5.8 million at the year’s start. While Chinese rival Deepseek has shown strong growth, its 6.2 million daily website visits in January fell far short of ChatGPT’s 117.5 million during the same period.
Ad
Despite billions of visitors, ChatGPT sends a trickle of traffic to source websites
Despite its massive user base, ChatGPT generates little outbound traffic, according to Similarweb. In the U.S., over the past six months, Reuters received just 50,900 referrals from ChatGPT – the highest among all news providers. The New York Post followed with 42,800 referrals, and The New York Times received 31,600.
These numbers reveal a striking but expected pattern: while ChatGPT has become one of the Internet’s most-visited sites, it sends very few users to its cited sources. Even the top 10 news sites combined, including the Wall Street Journal (27,400), Forbes (26,200), and Business Insider (23,900), received fewer than 300,000 total referrals over six months.
While OpenAI isn’t primarily a search engine, this minimal traffic sharing raises concerns. The company has formed multiple media partnerships to improve its sourcing, but users rarely review the original content. A recent study found that 96 percent of AI answer engine users never click on source links.
This behavior creates two problems: users don’t verify potentially incorrect information, and services like ChatGPT search and Google’s new AI search risk undermining the traditional web ecosystem.











